Infrared dim-small target detection via chessboard topology
Bingbing Dan, Zijian Zhu, Meihui Li and Tao Tang
Optics & Laser Technology, 2024.
[abstract]
[paper]
[code]
[bibtex]
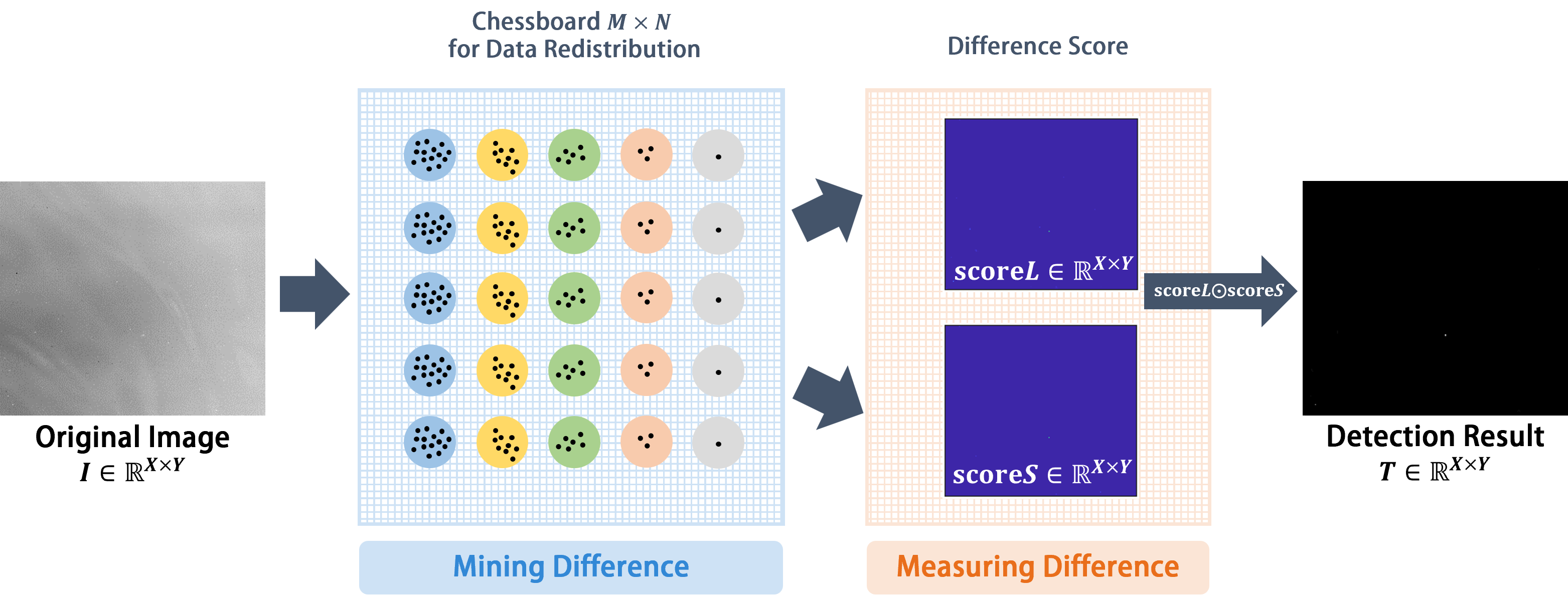
In infrared dim-small target detection, large background group and small clutter group are the key components. However, existing methods usually consider the detection progress in the original image space, which limits the separability of the target from the two components and leads to missed detection and false alarms. In response to this issue, we propose an innovative infrared dim-small target detection method via chessboard topology, which mines potential differences, such as distribution density and scale trends in the topological space. Specifically, the core of our approach lies in the construction of the chessboard topology space, where each ”point set” serves as a basic unit that is a mapping result of pixels in the original image space. The chessboard’s horizontal divisions are based on the scale space, where pixels undergo multiscale transformations to emphasize scale invariance at smaller scales, resulting in rows that capture scale variation trends. Meanwhile, the vertical divisions are based on the gray space, with pixels rearranged to accentuate gray level variations, thereby forming columns that highlight distribution density disparities. To separate the target pixels, we design two complementary strategies for pixel scoring within the chessboard topological space. The first, scoreS, evaluates pixel consistency across multiple scales, aiming to eliminate inconsistent pixels that often represent false positives. The second, scoreL, focuses on measuring the density level of point sets to enhance target visibility by filtering out pixels within less dense point sets. The final detection results are derived from the dot product of these two scores, ensuring a robust differentiation of small targets from background and noise. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed method achieves better performance than baselines in six real infrared dim-small target scenarios.
@article{dan2025infrared,
title={Infrared dim-small target detection via chessboard topology},
author={Dan, Bingbing and Zhu, Zijian and Wei, Yuxing and Liu, Dongxu and Li, Meihui and Tang, Tao},
journal={Optics \& Laser Technology},
volume={181},
pages={111867},
year={2025},
publisher={Elsevier}
}